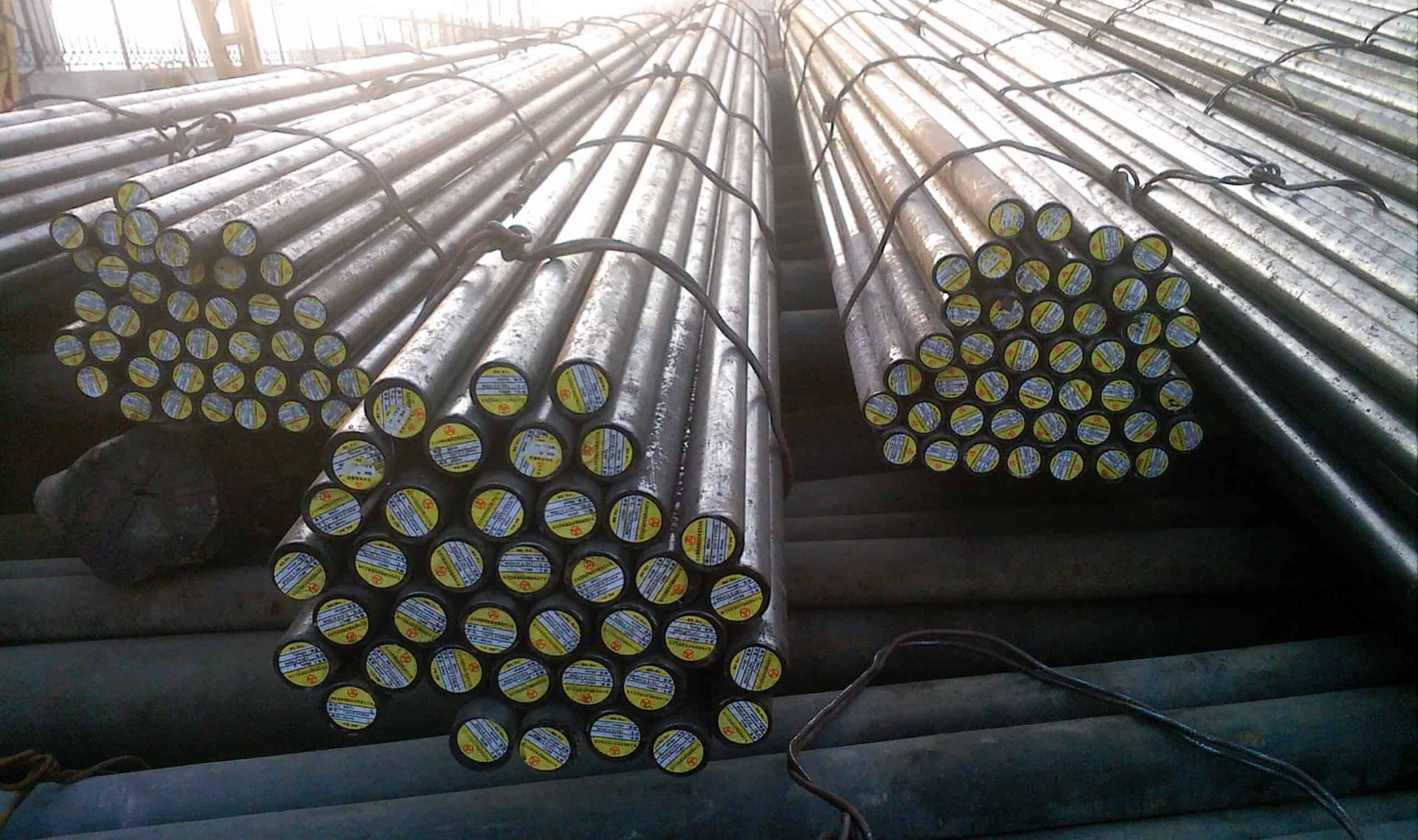
42CrMo4 / DIN 1.7225 Steel
42CrMo4 is a heat treatable steel which contains at least 0.9%Cr,0.15%Mo as strengthening elements.After quenched and tempered, It obtains high strength, good low-temperature impact toughness with a typical tensile strength of 900 -1200 N/mm2.42CrMo4 steel has better performance than 34CrMo4 steel due to the higher carbon and chromium content.Similar to AISI 4140,only a little difference in Mn,Cr content.This material also has good machinability,good wear-resistance,but the temper brittleness is not obvious,and poor in weldability.
42CrMo4 Supply Form & Size & Tolerance
| Form of Supply | Size(mm) | Length(mm) |
| Round bar | Φ6-Φ1,000 | 3,000-10,000 |
| Square bar | 100×100-600×600 | 3,000-6,000 |
| Plate/Sheet | Thickness :20-400 Width:80-1,000 |
2,000-6,000 |
| Flat bar/Blcoks | Thickness :120-800 Width:120-1,500 |
2,000-6,000 |
42CrMo4 Surface Finish&Tolerance
| Surface Finish | Black-Forged | Black-Rolled | Turned | Grinding | Polished | Peeled | Cold Drawn |
| Tolerance | (0,+5mm) | (0,+1mm) | (0,+3mm) | Best h9 | Best h11 | Best H11 | Best H11 |
42CrMo4 Chemical Composition per EN 10083-3
| GRADE | NUMBER | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo |
| 42CrMo4 | 1.7225 | 0.38-0.45 | ≤ 0.40 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤ 0.025 | ≤ 0.035 | 0.90-1.20 | 0.15-0.30 |
42CrMo4 Relevant Standards
| USA | UK | China | Japan | France | Russia |
| 4140 | EN19/708M40 | 42CrMo | SCM440 | 42CD4 | 42HM |
42CrMo4 Mechanical Property
| Diameter d mm | ≤ 16 | 16-40 | 40-100 | 100-160 | 160-250 |
| Thickness t mm | < 8 | 8-20 | 20-60 | 60-100 | 100-160 |
| Yield Strength Mpa | ≥900 | ≥750 | ≥650 | ≥550 | ≥500 |
| Tensile Strength Mpa | 1100-1300 | 1000-1200 | 900-1100 | 800-950 | 750-900 |
| Elongation, % | ≥10 | ≥11 | ≥12 | ≥13 | ≥14 |
| Reduction of area ,% | ≥40 | ≥45 | ≥50 | ≥50 | ≥55 |
| impact | ≥30 | ≥35 | ≥35 | ≥35 | ≥35 |
42CrMo4 Forging
42CrMo4 forging temperature:900 – 1100°C ,cooling as slowly as possible in still air or in sand after forged.
42CrMo4 Heat Treatment
- Normalizing: 850 – 880°C,Cooling in air
- Soft Annealing:680 – 720°C,Cooling in furnace
- Stress relieve:450-650°C,Cooling in air
- Hardening:820 – 880°C,oil or water quench
- Tempering:540 – 680°C,Cooling in air
42CrMo4 Surface Hardness
- Treated to improve shearability (+S):Max 255HB
- Soft annealed (+A):Max 241HB
- Pre Quenched and tempered:280-320HB
- Flame or induction hardening:Min 53HRC
| NORMAL HARDENABILITY +H (850°C – hardness HRC – distance mm) | |||||||||||||||
| Distance mm | 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 |
| HRC Min | 53 | 53 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 43 | 40 | 37 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 29 |
| HRC Max | 61 | 61 | 61 | 60 | 60 | 59 | 59 | 58 | 56 | 53 | 51 | 48 | 47 | 46 | 45 |
Key Features and Benefits
- High Strength and Toughness:
- Maintains mechanical integrity under high loads and shock.
- Wear Resistance:
- Chromium and molybdenum improve surface wear resistance, ideal for high-friction applications.
- Hardenability:
- Provides uniform hardness in larger cross-sections.
- Fatigue Resistance:
- Performs well in applications involving cyclic loading.
- Versatility:
- Adapts to various heat treatments, enabling tailored mechanical properties.
Applications of 42CrMo4 / 1.7225 Steel
42CrMo4 is extensively used in high-performance applications across multiple industries:
- Automotive Industry:
- Gears, axles, crankshafts, and connecting rods.
- Aerospace:
- Landing gear, structural parts, and engine components.
- Machinery Manufacturing:
- Hydraulic cylinders, spindles, and machine tool components.
- Oil and Gas Industry:
- Drill collars, rotary shafts, and high-pressure equipment.
- Construction Equipment:
- Pins, bushings, and heavy-duty components.
Heat Treatment of 42CrMo4 Steel
Heat treatment processes allow 42CrMo4 to achieve the desired balance of strength, hardness, and toughness:
- Annealing:
- Heated to 740–770°C, followed by slow cooling to improve machinability and reduce hardness.
- Normalizing:
- Heated to 840–880°C and air-cooled, refining the grain structure for enhanced toughness.
- Quenching and Tempering:
- Quenched at 820–860°C in oil or water, followed by tempering at 540–680°C to achieve high strength and toughness.
- Nitriding:
- Surface hardening at 500–550°C improves wear resistance and fatigue strength without altering the core properties.
- Stress Relieving:
- Performed at 550–650°C to reduce residual stresses after machining or welding.
Processing Techniques
- Machining:
- Best machined in annealed or normalized conditions. Carbide or high-speed steel tools are recommended for hardened states.
- Welding:
- Preheating to 200–300°C and post-weld stress relief are necessary to avoid cracking.
- Cold Working:
- Limited due to high strength; suitable for minor forming operations.
- Forging:
- Performed at 1,000–1,200°C, followed by air cooling or normalizing.
Comparisons with Similar Grades
| Steel Grade | 42CrMo4 (1.7225) | AISI 4140 | EN 19 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Content | Medium (0.38–0.45%) | Medium (0.38–0.43%) | Medium (0.36–0.44%) |
| Chromium Content | 0.90–1.20% | 0.80–1.10% | Similar |
| Molybdenum Content | 0.15–0.30% | 0.15–0.25% | Similar |
| Applications | High-stress parts | General engineering | High-performance parts |
Certifications and Standards
42CrMo4 steel adheres to multiple international standards:
- DIN EN 10083-3: Steels for quenching and tempering.
- ASTM A829: Structural alloy steel.
- SAE J404: Chemical compositions for alloy steels.
Other Related Steel
Page Contents
- 42CrMo4 Supply Form & Size & Tolerance
- 42CrMo4 Surface Finish&Tolerance
- 42CrMo4 Chemical Composition per EN 10083-3
- 42CrMo4 Relevant Standards
- 42CrMo4 Mechanical Property
- 42CrMo4 Forging
- 42CrMo4 Heat Treatment
- 42CrMo4 Surface Hardness
- Key Features and Benefits
- Applications of 42CrMo4 / 1.7225 Steel
- Heat Treatment of 42CrMo4 Steel
- Processing Techniques
- Comparisons with Similar Grades
- Certifications and Standards
- Other Related Steel