AISI 4140 Alloy Steel – ASTM A29
Are you looking for AISI 4140 alloy steel? WALDUN is the best AISI 4140 alloy steel Manufacturer and Exporter from China. You can get round,square,flat,block,and shaft etc. We are one of the largest manufacturers in China with over 15 years experience. Our products have been exported to many countries all around the world. With our own factory we can provide high quality products at a competitive price! If you want to buy or wholesale bulk AISI 4140 alloy steel in large quantities please contact us now! We will offer you unbeatable prices and service that cannot be matched by other suppliers! Please feel free to send us an inquiry if you need any help or more information about our company or services. We look forward to hearing from you soon! AISI 4140 alloy steel is defined as a low alloy steel which has 1% Cr-Mo as strengthening alloy elements.Compared with AISI 4130, it has a higher carbon content with good balance of strength, toughness ,abrasion and impact resistance and heat treatment capabilities,but poor in weldability characteristics.AISI 4140 is generally supplied in quenched and tempered condition with hardness 28-32HRC. 4140 steel is used to manufacture forgings with higher strength and larger quenched cross-section than 35CrMo steel, such as large gears for locomotive traction, supercharger transmission gears, rear axles, connecting rods and spring clips which are subject to great loads, and also used for oil deep well drill pipe joints and salvage tools below 2000m.
4140 Alloy Steel Supply Form & Size & Tolerance
| Supply Form | Size(mm) | Process | Tolerance | |
| Round | Φ6-Φ100 | Cold Drawn | Bright/Black | Best H11 |
| Φ16-Φ350 | Hot Rolled | Black | -0/+1mm | |
| Peeled/ground | Best H11 | |||
| Φ90-Φ1000 | Hot Forged | Black | -0/+5mm | |
| Rough Turned | -0/+3mm | |||
| Flat/Square/Block | Thickness :120-800 | Hot Forged | Black | -0/+8mm |
| Width:120-1500 | Rough Machined | -0/+3mm | ||
Remark:Tolerance can be customized as per requests
4140 Steel Chemical Composition
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo |
| ASTM A29 | 4140 | 0.38-0.43 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.75-1.00 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.04 | 0.8-1.1 | – | 0.15-0.25 |
| EN10083 | 42CrMo4 | 0.38-0.45 | ≤ 0.4 | 0.6-0.90 | ≤ 0.025 | ≤ 0.035 | 0.9-1.2 | – | 0.15-0.30 |
| 1.7225 | |||||||||
| JIS G4105 | SCM440 | 0.38-0.43 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.6-0.85 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.04 | 0.9-1.2 | – | 0.15-0.30 |
| GB 3077 | 42CrMo | 0.38-0.45 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.5-0.80 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 | 0.9-1.2 | – | 0.15-0.25 |
| BS 970 | EN19 | 0.35-0.45 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.5-0.80 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 | 0.9-1.5 | – | 0.2-0.40 |
4140 Steel Physical Property
| Density g/cm3 | 7.85 | ||||
| Melting point °C | 1416 | ||||
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.27-0.30 | ||||
| Machinability (AISI 1212 as 100% machinability) | 65% | ||||
| Thermal expansion co-efficient µm/m°C | 12.2 | ||||
| Thermal conductivity W/(m.K) | 46 | ||||
| Modulus of elasticity 10^3 N/mm2 | 210 | ||||
| Electric resistivity Ohm.mm2 /m | 0.19 | ||||
| Specific heat capacity J/(kg.K) | 460 | ||||
| Modulus of elasticity 10^3 N/mm2 | 100 ℃ | 200 ℃ | 300 ℃ | 400 ℃ | 500 ℃ |
| 205 | 195 | 185 | 175 | 165 | |
| Thermal expansion 10^6 m/(m.K) | 100 ℃ | 200 ℃ | 300 ℃ | 400 ℃ | 500 ℃ |
| 11.1 | 12.1 | 12.9 | 13.5 | 13.9 | |
4140 Steel Mechanical Property
| Mechanical Condition | R | S | S | T | U | V | W |
| Ruling Section mm | 250 | 250 | 150 | 100 | 63 | 30 | 20 |
| Tensile Strength Mpa | 700-850 | 770-930 | 770-930 | 850-1000 | 930-1080 | 1000-1150 | 1080-1230 |
| Yield Strength Mpa Min | 480 | 540 | 570 | 655 | 740 | 835 | 925 |
| Elongation % | 15 | 13 | 15 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Izod Impact J Min | 34 | 27 | 54 | 54 | 47 | 47 | 40 |
| Charpy Impact J Min | 28 | 22 | 50 | 50 | 42 | 42 | 35 |
| Hardness Brinell HB | 201-255 | 233-277 | 233-277 | 248-302 | 269-331 | 293-352 | 311-375 |
4140 Steel High Temperature Strength
| For quenched and tempered heavy forgings | |||||||
| Diameter mm | Yield strength MPa | ||||||
| 20 ℃ | 100 ℃ | 200 ℃ | 250 ℃ | 300 ℃ | 350℃ | 400℃ | |
| ≤250 | 510 | 486 | 461 | 441 | 422 | 392 | 363 |
| 250-500 | 460 | 431 | 412 | 402 | 382 | 353 | 324 |
| 500-750 | 390 | 333 | 333 | 324 | 304 | 275 | 245 |
4140 Steel Forging
Forging temperature should be carried out between 900℃-1200℃,The lower the forging-ending temperature ,the finer the grain size .Hold the temperature till uniform before forge,minimum forging temperature 850°C,so don’t forge below 850℃.AISI 4140 steel should be cooled as slowly as possible in still air or in sand after forged.
4140 Steel Normalizing
Normalizing is used to refine the structure of forgings that might have cooled non-uniformly after forged,and considered as a conditioning treatment before final heat treatment.Normalizing temperature for AISI 4140 steel should be carried out between 870℃-900℃. hold suitable time for the steel to be thoroughly heated to complete the ferrite to austenite transformation.Cool in still air.
4140 Steel Annealing
After Forged,AISI 4140 steel may be annealed .Annealing temperature should be carried out between 800℃-850℃, hold suitable time for the steel to be thoroughly heated. Cool slowly in the furnace.This treatment will form a structure suitable for machining.The maximum Hardness is 241 HB.
4140 Steel Hardening
This heat treatment will obtain martensite structure after quenched.It should be carried out between 840℃-875℃, hold suitable time for the steel to be thoroughly heated, soak for 10-15 minutes per 25 mm section, and quench in oil, water, or polymer as required.Tempering should be followed immediately after quenched.
4140 Steel Tempering
Tempering is usually carried out to relieve stresses from the hardening process, but primarily to obtain the required hardness and mechanical properties. The actual tempering temperature will be chosen to meet the required properties.Heat the AISI 4140 carefully to a suitable temperature ,usually between 550℃-700℃, soak at the temperature for 2 hours per 25mm of ruling section, then cool in air.Tempering between 250℃-375℃ is not avoided as tempering within this range will seriously reduce the impact value,result in temper brittleness .
4140 Steel Application
AISI 4140 steel finds many applications as forgings for the aerospace,oil and gas,automotive, agricultural and defense industries etc. Typical applications for 4140 steel uses include:forged gears,spindles,fixtures,jigs,collars,Axles,conveyor parts,crow bars,logging parts,shafts,sprockets,studs,pinions,pump shafts, rams, and ring gears etc
SAE 4140 VS AISI 4140
With the increasing international trade volume of steel materials, SAE/AISI steel grade codes are often encountered in inquiries, such as the common AISI 4140 and SAE 4140, SAE 1045 and AISI 1045, AISI 4340 and SAE 4340 and so on.
So the question is, do they represent the same material?
First, we need to clarify that AISI and SAE stand for the American Iron and Steel Institute (A.I.S.I.) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (S.A.E.).These two associations participated in the standardization of the steel numerical coding system, and gradually integrated into the AISI/SAE steel grade nomenclature joint system.

The value of SAE/AISI is that technical engineers can obtain general information (though not comprehensive) about steel types and their grades through this steel grade nomenclature system.So far, the steel grade codes of SAE and AISI are often quoted in the quotation and product certification of steel products in the United States, without deliberately distinguishing them.
Therefore, from the above, it can be seen that “4140”, “AISI 4140” or “SAE 4140”, although written differently, but in most general industrial applications,any of the above is considered equivalent.
Critical Temperature for Heat Treatment of SAE 4140
- Ac1:730℃
- Ac3:780℃
- Ar1:690℃
- Ms:360℃
Heat Treatment For SAE 4140
- Normalizing
After hot working, SAE 4140 normalizing,can refine the grains, homogenize the structure, and prepare the structure for the final heat treatment(Especially for Q&T).
Process Details:
- Normalizing temperature:840-880°C
- Heating and heat preservation in steps at 450°C,650°C
- Controlling the heating speed to ensure uniform heating.
- Air cooling,which can be accelerated by blowing air or water mist.
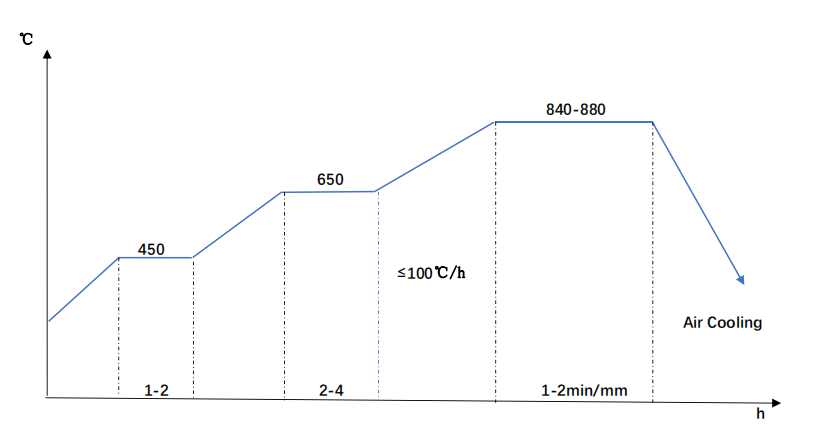
SAE 4140 Normalizing Diagram
- Annealing
For the annealing of SAE 4140, the main purpose is to reduce hardness, improve machinability and reduce residual stress.
Common annealing methods are generally divided into the following types.
- Complete annealing (recrystallization annealing):800-850°C
- Isothermal annealing:675°C
- Stress relief annealing:600-650°C
Cooling Method:Furnace Cooling
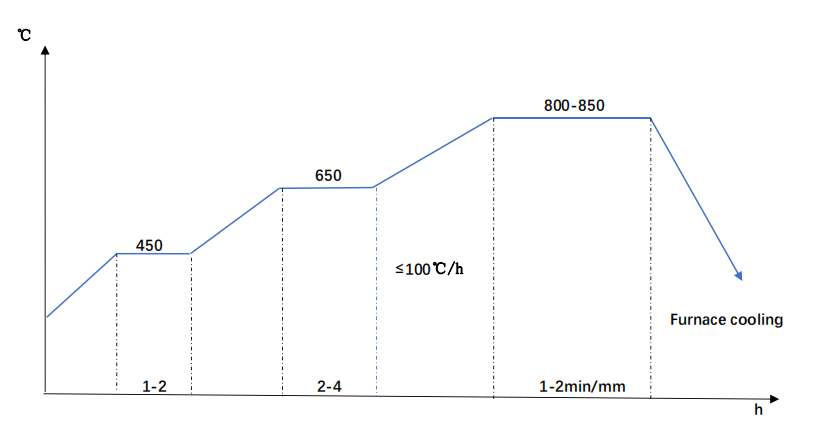
SAE 4140 Annealing Diagram
- Quenching & Tempering(QT) For SAE 4140
Quenching and tempering refers to a heat treatment process used to improve the comprehensive mechanical properties of steel materials. That is, after quenching, it is subjected to high temperature tempering treatment.
For SAE 4140 steel,the purpose of quenching and tempering is to make the material obtain a good combination of strength and toughness, which not only has high strength, but also has excellent toughness, plasticity, and cutting performance.
Process Details:
1.Quenching temperature:840-880°C
2.Hold at this temperature then quench in oil or water
3.Tempering as soon as possible when the temperature low to ambient
4.Heat uniformly to the suitable temperature of 540-680°C
5.keep the material out of the furnace ,then cool in the air
Quenching Hardness:55-59HRC
Tempering temperature:220-650°C,Corresponding hardness:28-58HRC.
Mechanical Property For SAE 4140 in Quenched and Tempered condition
1.Tensile strength: ≥1100MPa
2.Yield point:≥950MPa
3.Percentage reduction of area after fracture: ≥45%
4.Elongation after fracture: ≥12%
5.Impact test (+20°C): Transverse – 26~42J; Longitud – 49~55J
Delivery Condition
1.Shape:Round/Square / Flat/Shafts/Rollers/Blocks
2.Surface condition:Black surface/Bright surface
3.Heat Treatment:Normalized/Annealed/QT
4.Straightness:Max 3mm/m(Enhanced straightness may be available on request)
5.Length:3000-5800mm suitable for 20″container. above 6000mm,suitable for 40″ container
6.Grain Size: 5-8 acc to ASTM E112-96
7.Ultrasonic Standard: Sep1921/ASTM A388/EN 10228-3
8.Typical Hardness:HB269-302
9.Non Metallic Inclusion: 2 max acc to ASTM E45 /K4≤20 acc to DIN 50602
10.Forging Ratio: minimum 4 : 1
11.Ingot Melting:EAF+LF+VD
12.Marking: Grade/Weight/Length/Size/Heat Number
Quality Certification
A material test report(Inspection Certificate EN 10204 3.1) will be provided, documenting the following:
1.Chemical analysis
2.Mechanical properties
3.Surface hardness
4.Non Metallic Inclusion
5.Heat Treatment Process
6.Grain size
7.Forging ratio
8.Ultrasonic test report
Supply Size & Condition For SAE 4140
- Round Bars: Dia.80 – 1,000mm as Forged
- Flat / Square Bars: Thickness Max.800mm
- Shafts, Rollers, Blocks: Customized or According to Drawing
- Rolled Round Bars: Dia.14 – 350mm with UT Assurance
Heat treatment:Quenched and Tempered (+QT), Normalizing (+N), Annealing (+A)
Surface finish:Black / Rough turned / Peeled
Page Contents
- 4140 Alloy Steel Supply Form & Size & Tolerance
- 4140 Steel Chemical Composition
- 4140 Steel Physical Property
- 4140 Steel Mechanical Property
- 4140 Steel High Temperature Strength
- 4140 Steel Forging
- 4140 Steel Normalizing
- 4140 Steel Annealing
- 4140 Steel Hardening
- 4140 Steel Tempering
- 4140 Steel Application
- SAE 4140 VS AISI 4140
- Critical Temperature for Heat Treatment of SAE 4140
- Heat Treatment For SAE 4140
- Process Details:
- Mechanical Property For SAE 4140 in Quenched and Tempered condition
- Delivery Condition
- Quality Certification
- Supply Size & Condition For SAE 4140












